Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
Posted on May 10th, 2016
What is CBT?
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy or CBT is a psychotherapy that recognises that the way we think (cognitions) and what we do (behaviour) affects how we feel (emotions). It is not the situation or the event that we are experiencing that creates our feelings, but the meaning we place upon the situation or the way we interpret the event that affects the way we feel. 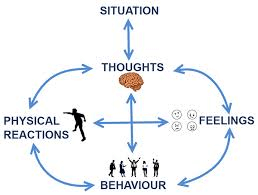
For example:
Event: You get called into your boss’s office.
Thought 1: Oh no, he’s going to fire me
Feeling: Anxious, sad, angry.
OR
Thought 2: He’s going to tell me what a great job I did yesterday
Feeling: happy, pleased.
The event itself has not changed, it is the meaning we place upon the event (the way we are thinking about it) that changes the way we feel.
What does this mean?
This is great news! What this means is that regardless of what is happening around us we still have the ability to manage our feelings. However, that is not to say that the event or situation does not influence what we think, of course it does. But ultimately the power is still up to us.
CBT is a structured therapy that teaches us a step by step process of how to challenge our thoughts and manage our feelings more effectively.
CBT is not about being overly rosy and positive, because that can be as unhelpful as being really negative. CBT focusses on balanced thinking and coping skills improvement. By using CBT a psychologist can teach you both cognitive and behavioural skills to improve how you feel and behave.
What can CBT be used to treat?
CBT is a leading form of psychological therapy in Australia. CBT is very effective in the treatment of many emotional, psychological and psychiatric conditions including:
- Depression
- Anxiety, OCD, PTSD, Social Anxiety, Phobias
- Worry
- Stress
- Anger
- Pain Management
The benefits of CBT
- can be a short term therapy
- individualised to meet your needs
- goal oriented
- based on empirical research
- long term results
CBT is an active ‘doing’ therapy; it’s much more than just talking.

